
Furthermore, individual carbon-to-carbon bonds may be single, double, or triple covalent bonds, and each type of bond affects the geometry of the molecule in a specific way. Which of the following statements is false? As the backbone of the large molecules of living things, hydrocarbons may exist as linear carbon chains, carbon rings, or combinations of both.
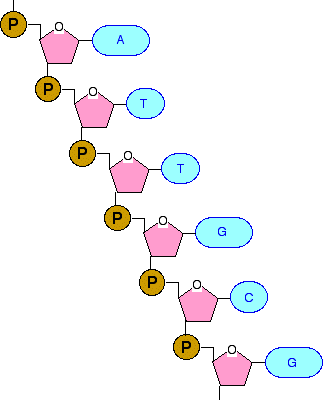
Since DNA strands of the helix run anti. When nucleotides connect to form DNA or RNA, the phosphate of one nucleotide attaches via a phosphodiester bond to the 3-carbon of the sugar of the next nucleotide, forming the sugar-phosphate backbone of the nucleic acid.
#Dna carbon backbone free
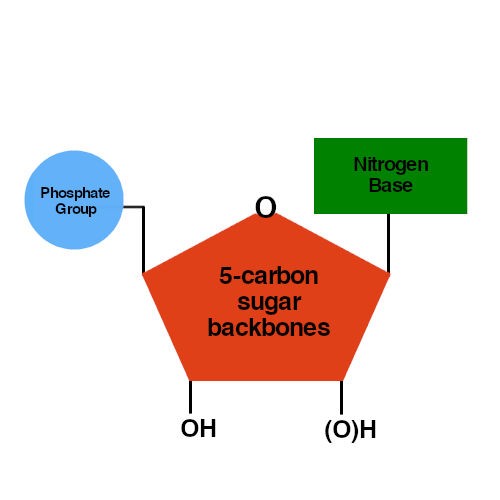
(c) Enantiomers are mirror images of each other. The sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA has the phosphate on the 5 carbon linked to the 3 carbon of the next sugar. A free nucleotide may have one, two, or three phosphate groups attached as a chain to the 5-carbon of the sugar. (b) Geometric isomers have a different arrangement of atoms around a double bond. (a) Structural isomers have a different covalent arrangement of atoms. When phosphate groups link together to form chains, as in ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the link looks like O-P-O-P-O-P-O, with two additional oxygen atoms attached to each phosphorus, one on either side of the atom.\): Molecules that have the same number and type of atoms arranged differently are called isomers. The nitrogenous bases are stacked in the interior, like a pair of staircase steps. One atom of oxygen is connected to the 5-carbon in the sugar and to the phosphorus atom. The sugar and phosphate lie on the outside of the helix, forming the DNAs backbone. DNA is made of four types of nucleotides, which are linked covalently into a polynucleotide chain (a DNA strand) with a sugar-phosphate backbone from which the.

Nitrogenous bases, which are bound to the deoxyribose groups, protrude. The only difference between them is that 2'-deoxyribose has one less oxygen atom attached to the second carbon.Ī single phosphate group is PO 4 3-. The deoxyribose and the phosphate groups form the backbone of the nucleic acid molecule. The carbons are numbered sequentially, to help keep track of where groups are attached. These monomers that are linked through phosphodiester bonds become the phosphate-sugar backbone of nucleic acids. Both ribose and deoxyribose are 5-carbon sugars. In RNA, the bases are adenine, guanine, uracil, and cytosine. In DNA, the bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). Cytosine, thymine, and uracil are pyrimidines.

Four carbons and an oxygen make up the five-membered ring the other carbon branches off the. Purines and pyrimidines are the two categories of nitrogenous bases. Roles of DNA and RNA in cells Nucleic acids, macromolecules made out of units called nucleotides, come in two naturally occurring varieties: deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) and ribonucleic acid ( RNA ). The deoxyribose sugar in DNA is a pentose, a five-carbon sugar.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
